Calgary by night

In front with Bow River
Coal Price
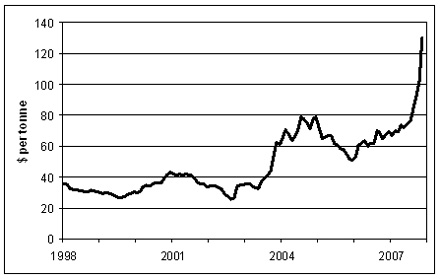
Increasing rapidly like Oil Price
Average Price of Electricity with Solar panel cost at $1/Wp as of now 2010 Violet curve
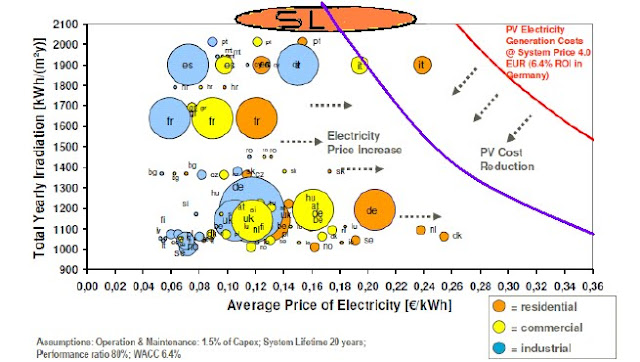
Sunday, December 30, 2012
Solar PV’s 44% Efficiency Record, Thanks To NREL & Solar Junction
Switch to HTML mode and paste the embed code over this text
Saturday, December 29, 2012
Friday, December 14, 2012
Monday, November 26, 2012
Thursday, November 1, 2012
chandigarh_solar_city_master_plan.pdf (application/pdf Object)
chandigarh_solar_city_master_plan.pdf (application/pdf Object)
In India, it is seen that every year there is an increase of 20-30% in energy requirement in the residential sector and 8-10% increase in commercial sector; leading to a situation where there are both, energy as well as peak deficits. In case of Chandigarh, as per Department of Environment, Chandigarh Administration, per capita electricity consumption has been reported as 1162 kWh in 2006-07. The projections shows gradual increase in per capita electricity consumption of the city and might be 1246 kWh in 2008. The total electricity consumption of the city has been reported as 1157.5 MU during 2007-08. Taking in to account the exponentially increasing energy demand, it became obvious to Chandigarh Union Territory that this trend is not sustainable in the long run. It felt that measures such as reducing energy demands and switching from fossil fuel to renewable energy technologies would go a long way in addressing these concerns.
As has been the case with the wide-scale introduction of renewable energy technologies for a variety of applications in the country; Chandigarh UT took initiative to develop Chandigarh city as a solar city. The Chandigarh Renewable Energy, Science and Technology Promotion Society (CREST) had been given the mandate to prepare the plan to achieve this objective. In essence, the Solar City programme strives to integrate:
Energy conservation measures to reduce the energy demand, and
Utilization of locally available resources such as solar energy to meet these reduced energy demands
This Master Plan for Solar City is a dynamic document meant to change with time, experience, and need. The development of master plan has benefited from the active participation of CREST, Public Works Department, Municipal Corporation UT, Chandigarh Administration, Municipal Water Supply Department, Forest Department, power utilities, electricity department of Chandigarh Administration; and other agencies with energy-related responsibilities.
The whole exercise of developing a Master Plan for making Chandigarh a solar city has been a collaborative endeavour along with all the major stakeholders in the city. Developing the city as a solar city requires an integrated urban planning approach, which simultaneously involves reducing reliance on fossil fuels by the application of energy conservation and efficiency measures and by replacing/complementing the
In India, it is seen that every year there is an increase of 20-30% in energy requirement in the residential sector and 8-10% increase in commercial sector; leading to a situation where there are both, energy as well as peak deficits. In case of Chandigarh, as per Department of Environment, Chandigarh Administration, per capita electricity consumption has been reported as 1162 kWh in 2006-07. The projections shows gradual increase in per capita electricity consumption of the city and might be 1246 kWh in 2008. The total electricity consumption of the city has been reported as 1157.5 MU during 2007-08. Taking in to account the exponentially increasing energy demand, it became obvious to Chandigarh Union Territory that this trend is not sustainable in the long run. It felt that measures such as reducing energy demands and switching from fossil fuel to renewable energy technologies would go a long way in addressing these concerns.
As has been the case with the wide-scale introduction of renewable energy technologies for a variety of applications in the country; Chandigarh UT took initiative to develop Chandigarh city as a solar city. The Chandigarh Renewable Energy, Science and Technology Promotion Society (CREST) had been given the mandate to prepare the plan to achieve this objective. In essence, the Solar City programme strives to integrate:
Energy conservation measures to reduce the energy demand, and
Utilization of locally available resources such as solar energy to meet these reduced energy demands
This Master Plan for Solar City is a dynamic document meant to change with time, experience, and need. The development of master plan has benefited from the active participation of CREST, Public Works Department, Municipal Corporation UT, Chandigarh Administration, Municipal Water Supply Department, Forest Department, power utilities, electricity department of Chandigarh Administration; and other agencies with energy-related responsibilities.
The whole exercise of developing a Master Plan for making Chandigarh a solar city has been a collaborative endeavour along with all the major stakeholders in the city. Developing the city as a solar city requires an integrated urban planning approach, which simultaneously involves reducing reliance on fossil fuels by the application of energy conservation and efficiency measures and by replacing/complementing the
Saturday, October 27, 2012
Solar Photovoltaics | HeatSpring Magazine Solar Photovoltaics | HeatSpring Magazine Residential Solar PV Design 101 http://blog.heatspring.com/category/solar-photovoltaics/
Solar Photovoltaics | HeatSpring Magazine
In this guide you will learn
1. Solar Basics: Power, Energy, Current, Resistance, Circuits,
Irradiance, Irradiation, Azmith, Horizontal Tilt, Declincation, Voc,
Vmp, Imp, Isc, Temperature and Voltage Relationship, Irradiance
and Current Relationship
2. How to Size an Array based customer constraints and site
constraints and how to estimate power production.
3. How to Design and Size Grid-Connected Solar PV Inverter, Size
Strings and Size Conductor
In this guide you will learn
1. Solar Basics: Power, Energy, Current, Resistance, Circuits,
Irradiance, Irradiation, Azmith, Horizontal Tilt, Declincation, Voc,
Vmp, Imp, Isc, Temperature and Voltage Relationship, Irradiance
and Current Relationship
2. How to Size an Array based customer constraints and site
constraints and how to estimate power production.
3. How to Design and Size Grid-Connected Solar PV Inverter, Size
Strings and Size Conductor
Thursday, October 25, 2012
Saturday, October 20, 2012
Sunday, September 30, 2012
NEW POWEr cOST cOMPAriSONS Levelised Cost of Electricity for a Range of New Power Generating Technologies
www.garnautreview.org.au/update-2011/commissioned-work/new-power-cost-comparisons.pdf
The capital cost of Solar PV has dropped faster so these figure will have to adjusted.

The capital cost of Solar PV has dropped faster so these figure will have to adjusted.
Welcome, PVOutput is a free service for sharing and comparing PV output data. If you own a solar system please contribute your power output readings.
India | Map
Welcome, PVOutput is a free service for sharing and comparing PV output data.
If you own a solar system please contribute your power output readings.
Saturday, September 29, 2012
Electricity Generation Cost Model - 2011 Update Revision 1 Department for Energy and Climate Change
www.decc.gov.uk/assets/decc/11/about-us/economics-social-research/2127-electricity-generation-cost-model-2011.pdf
Electricity Generation Cost
Model - 2011 Update
Revision 1
Department for Energy and
Climate Change
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This report provides the supporting information to the update of cost assumptions and technical inputs
for the DECC Levelised Electricity Cost Model.
The report begins by defining the scope of the work which PB undertook and the general limitations
which were experienced. The methodology of the work, including the general approach and the data
sources used, are then detailed. Also, any fundamental changes which had to be made to the model
are explained.
The main focus of the report is an analysis of the methods and assumptions used to update the cost
and technical inputs. The main parameters of key timings, technical data, capital costs and operation
and maintenance (O&M) costs are discussed in full.
The report is concluded by giving an overview of each technology, in terms of the notable updates
and key reasons behind these updates. The current state of the technology and any expected future
changes are also discussed.
A summary of the updated cost assumptions and technical inputs have been included in the
appendices of the report, along with the subsequent levelised cost results
Electricity Generation Cost
Model - 2011 Update
Revision 1
Department for Energy and
Climate Change
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This report provides the supporting information to the update of cost assumptions and technical inputs
for the DECC Levelised Electricity Cost Model.
The report begins by defining the scope of the work which PB undertook and the general limitations
which were experienced. The methodology of the work, including the general approach and the data
sources used, are then detailed. Also, any fundamental changes which had to be made to the model
are explained.
The main focus of the report is an analysis of the methods and assumptions used to update the cost
and technical inputs. The main parameters of key timings, technical data, capital costs and operation
and maintenance (O&M) costs are discussed in full.
The report is concluded by giving an overview of each technology, in terms of the notable updates
and key reasons behind these updates. The current state of the technology and any expected future
changes are also discussed.
A summary of the updated cost assumptions and technical inputs have been included in the
appendices of the report, along with the subsequent levelised cost results
Friday, September 28, 2012
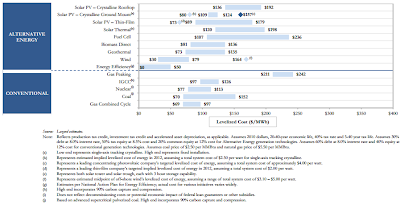
L E V E L I Z E D C O S T O F E N E R G Y A N A L Y S I S – V E R S I O N 5 . 0
votesolar.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/Lazard-June-11-Levelized-Cost-of-Energy-and-proj-to-2020-copy.pdf
L E V E L I Z E D C O S T O F E N E R G Y A N A L Y S I S – V E R S I O N 5 . 0
Levelized Cost of Energy Comparison
2
Certain Alternative Energy generation technologies are becoming increasingly cost-competitive with conventional generation
technologies under some scenarios, before factoring in environmental and other externalities (e.g., RECs, transmission and
back-up generation/system reliability costs) as well as construction and fuel costs dynamics affecting conventional generation
technologies
L E V E L I Z E D C O S T O F E N E R G Y A N A L Y S I S – V E R S I O N 5 . 0
Levelized Cost of Energy Comparison
2
Certain Alternative Energy generation technologies are becoming increasingly cost-competitive with conventional generation
technologies under some scenarios, before factoring in environmental and other externalities (e.g., RECs, transmission and
back-up generation/system reliability costs) as well as construction and fuel costs dynamics affecting conventional generation
technologies
Levelized Cost of Solar Photovoltaics in North Carolina
energync.org/assets/files/LCOE of Solar PV in North Carolina-FINAL.pdf
Key findings from this report include:
For many electric utilities, solar PV systems greater than 10 kW with federal and state tax credits were at grid
parity or cost competitive with commercial retail electricity prices in North Carolina in 2011.
Solar PV systems greater than 500 kW with federal and state tax credits achieve grid parity or become cost
competitive with commercial retail electricity prices for all North Carolina electric utilities in 2015.
Solar PV systems greater than 10 kW through 500 kW with federal and state tax credits achieve grid parity or
become cost competitive with commercial retail electricity prices for all North Carolina electric utilities in 2018.
Solar PV systems 10 kW or less taking federal and state tax credits achieve grid parity or become cost
competitive with residential retail electricity prices for the majority of North Carolina electric utilities in 2020.
For many electric utilities, solar PV without federal and state tax credits will be at grid parity or cost competitive
with retail electricity prices in North Carolina in 2020.
Key findings from this report include:
For many electric utilities, solar PV systems greater than 10 kW with federal and state tax credits were at grid
parity or cost competitive with commercial retail electricity prices in North Carolina in 2011.
Solar PV systems greater than 500 kW with federal and state tax credits achieve grid parity or become cost
competitive with commercial retail electricity prices for all North Carolina electric utilities in 2015.
Solar PV systems greater than 10 kW through 500 kW with federal and state tax credits achieve grid parity or
become cost competitive with commercial retail electricity prices for all North Carolina electric utilities in 2018.
Solar PV systems 10 kW or less taking federal and state tax credits achieve grid parity or become cost
competitive with residential retail electricity prices for the majority of North Carolina electric utilities in 2020.
For many electric utilities, solar PV without federal and state tax credits will be at grid parity or cost competitive
with retail electricity prices in North Carolina in 2020.
Thursday, September 27, 2012
[தமிழ் மன்றம்] Re: [தந்தை பெரியார்] கூடங்குளம் அணு உலையும், மின் தடையில்லா தமிழகம் என்ற மாயையும்…………மொழியாக்கம் – நற்றமிழன் - தமிழ் மன்றம் | Google Groups
Tuesday, September 11, 2012
Tuesday, August 28, 2012
Friday, August 10, 2012
Thursday, August 9, 2012
Tuesday, July 24, 2012
Water Can Store Information - YouTube
Water Can Store Information - YouTube: "Researchers have uncovered methods of proving water not only has a memory, but one that can be effected by your consciousness. It is a liquid crystal, it can record memories and impressions just like a disk drive. Water picks up emotions, thoughts, intentions, and more from its environment."
'via Blog this'
'via Blog this'
How the frozen water crystals are photographed - YouTube
How the frozen water crystals are photographed - YouTube: "How the frozen water crystals are photographed"
'via Blog this'
'via Blog this'
Monday, July 23, 2012
Thursday, June 28, 2012
Wednesday, April 18, 2012
Saturday, April 14, 2012
Monday, April 9, 2012
Monday, April 2, 2012
Tuesday, March 6, 2012
London Hindu Temples: Complete works of Swami Vivekanada Vol - 1
London Hindu Temples: Complete works of Swami Vivekanada Vol - 1: For the first time in History,as has been said elsewhere, hinduism itself forms here the subject of generalisation of a hindu mind of t...
Sunday, March 4, 2012
Energy security vital for development Financial News | Sundayobserver.lk
Financial News | Sundayobserver.lk
Energy security vital for development - By Lalin FERNANDOPULLE Dr. Nishantha Nanayakkara
Energy security vital for development - By Lalin FERNANDOPULLE Dr. Nishantha Nanayakkara
Saturday, March 3, 2012
Thursday, March 1, 2012
Wednesday, February 29, 2012
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Monday, February 27, 2012
Monday, February 20, 2012
Saturday, February 18, 2012
ao_DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF PHOTOVOLTAIC WATER PUMPING SYSTEM
ao_thesis.pdf (application/pdf Object)
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF PHOTOVOLTAIC WATER PUMPING SYSTEM
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF PHOTOVOLTAIC WATER PUMPING SYSTEM
Wednesday, February 15, 2012
A New Solar / Wind Charge Controller Based on the 555 Chip
A New Solar / Wind Charge Controller Based on the 555 Chip
http://www.mdpub.com/555Controller/images/powersystem2.jpg
http://www.mdpub.com/555Controller/images/powersystem2.jpg
Monday, January 23, 2012
Sunday, January 22, 2012
Friday, January 20, 2012
Thursday, January 19, 2012
Tuesday, January 3, 2012
Sunday, January 1, 2012
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)