Calgary by night

In front with Bow River
Coal Price
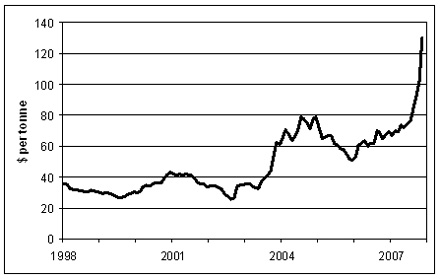
Increasing rapidly like Oil Price
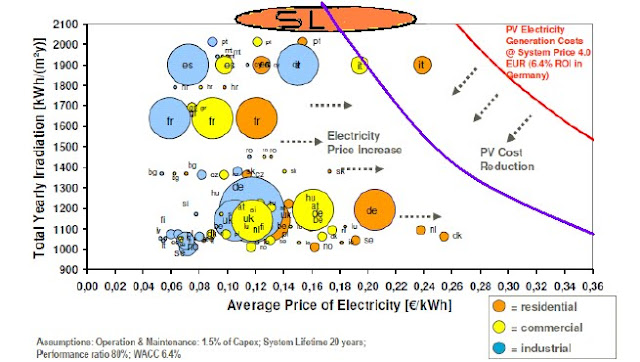
Average Price of Electricity with Solar panel cost at $1/Wp as of now 2010 Violet curve
Monday, November 26, 2012
Thursday, November 1, 2012
chandigarh_solar_city_master_plan.pdf (application/pdf Object)
chandigarh_solar_city_master_plan.pdf (application/pdf Object)
In India, it is seen that every year there is an increase of 20-30% in energy requirement in the residential sector and 8-10% increase in commercial sector; leading to a situation where there are both, energy as well as peak deficits. In case of Chandigarh, as per Department of Environment, Chandigarh Administration, per capita electricity consumption has been reported as 1162 kWh in 2006-07. The projections shows gradual increase in per capita electricity consumption of the city and might be 1246 kWh in 2008. The total electricity consumption of the city has been reported as 1157.5 MU during 2007-08. Taking in to account the exponentially increasing energy demand, it became obvious to Chandigarh Union Territory that this trend is not sustainable in the long run. It felt that measures such as reducing energy demands and switching from fossil fuel to renewable energy technologies would go a long way in addressing these concerns.
As has been the case with the wide-scale introduction of renewable energy technologies for a variety of applications in the country; Chandigarh UT took initiative to develop Chandigarh city as a solar city. The Chandigarh Renewable Energy, Science and Technology Promotion Society (CREST) had been given the mandate to prepare the plan to achieve this objective. In essence, the Solar City programme strives to integrate:
Energy conservation measures to reduce the energy demand, and
Utilization of locally available resources such as solar energy to meet these reduced energy demands
This Master Plan for Solar City is a dynamic document meant to change with time, experience, and need. The development of master plan has benefited from the active participation of CREST, Public Works Department, Municipal Corporation UT, Chandigarh Administration, Municipal Water Supply Department, Forest Department, power utilities, electricity department of Chandigarh Administration; and other agencies with energy-related responsibilities.
The whole exercise of developing a Master Plan for making Chandigarh a solar city has been a collaborative endeavour along with all the major stakeholders in the city. Developing the city as a solar city requires an integrated urban planning approach, which simultaneously involves reducing reliance on fossil fuels by the application of energy conservation and efficiency measures and by replacing/complementing the
In India, it is seen that every year there is an increase of 20-30% in energy requirement in the residential sector and 8-10% increase in commercial sector; leading to a situation where there are both, energy as well as peak deficits. In case of Chandigarh, as per Department of Environment, Chandigarh Administration, per capita electricity consumption has been reported as 1162 kWh in 2006-07. The projections shows gradual increase in per capita electricity consumption of the city and might be 1246 kWh in 2008. The total electricity consumption of the city has been reported as 1157.5 MU during 2007-08. Taking in to account the exponentially increasing energy demand, it became obvious to Chandigarh Union Territory that this trend is not sustainable in the long run. It felt that measures such as reducing energy demands and switching from fossil fuel to renewable energy technologies would go a long way in addressing these concerns.
As has been the case with the wide-scale introduction of renewable energy technologies for a variety of applications in the country; Chandigarh UT took initiative to develop Chandigarh city as a solar city. The Chandigarh Renewable Energy, Science and Technology Promotion Society (CREST) had been given the mandate to prepare the plan to achieve this objective. In essence, the Solar City programme strives to integrate:
Energy conservation measures to reduce the energy demand, and
Utilization of locally available resources such as solar energy to meet these reduced energy demands
This Master Plan for Solar City is a dynamic document meant to change with time, experience, and need. The development of master plan has benefited from the active participation of CREST, Public Works Department, Municipal Corporation UT, Chandigarh Administration, Municipal Water Supply Department, Forest Department, power utilities, electricity department of Chandigarh Administration; and other agencies with energy-related responsibilities.
The whole exercise of developing a Master Plan for making Chandigarh a solar city has been a collaborative endeavour along with all the major stakeholders in the city. Developing the city as a solar city requires an integrated urban planning approach, which simultaneously involves reducing reliance on fossil fuels by the application of energy conservation and efficiency measures and by replacing/complementing the
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)